Fermentation, Free Full-Text
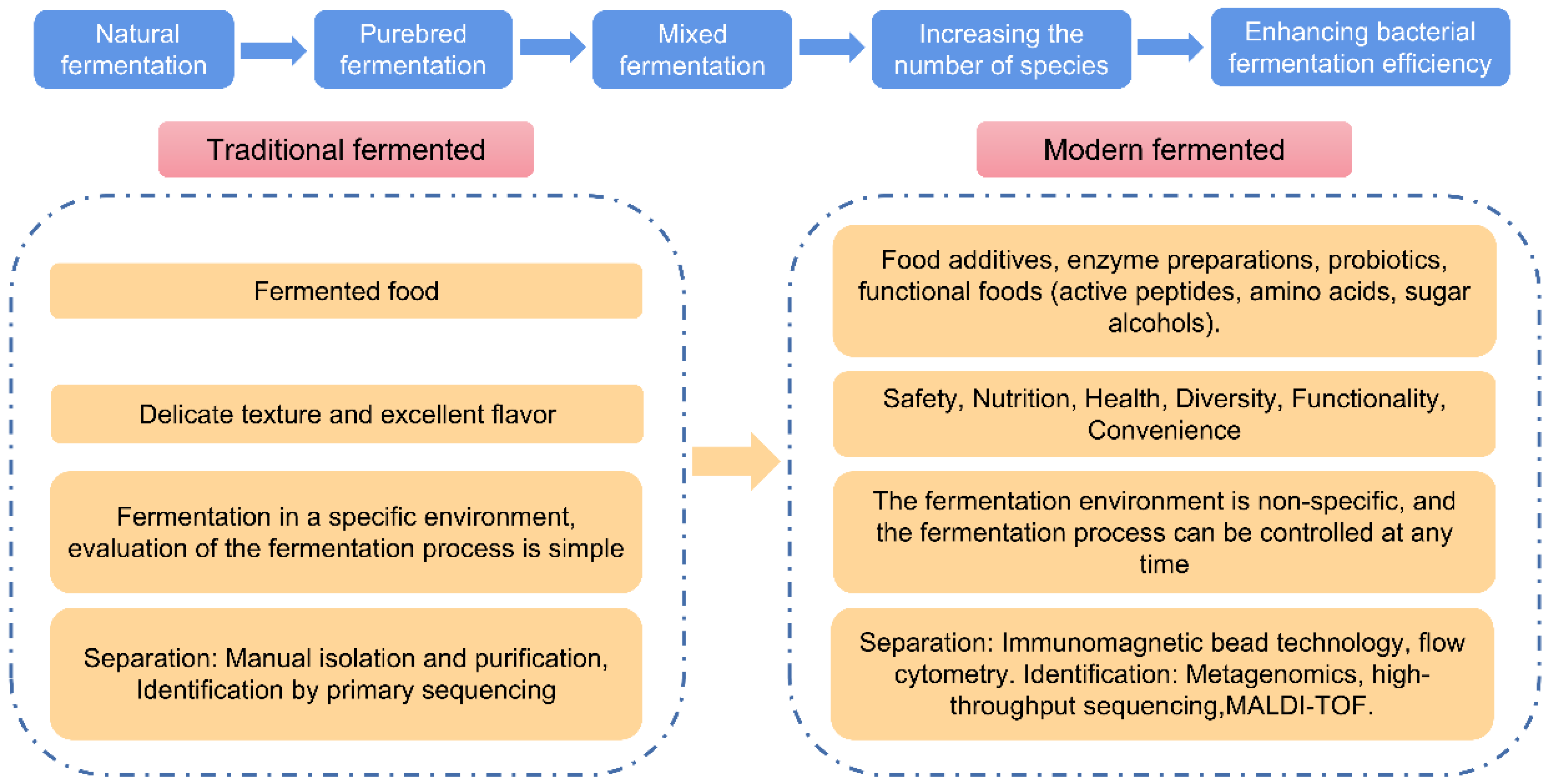
Fermentation technology has a long history and low-temperature fermentation has now become the focus of research. This paper reviews the mechanism and application of low-temperature fermentation and the optimization of relevant strains. Low-temperature fermentation leads to a differential expression of growth in metabolism genes (PSD1, OPI3, ERG3, LCB3 and NTH1). Low-temperature fermentation can be applied to foods and has various advantages, such as increasing changes in volatile flavor compounds and other corresponding metabolic substances of the strain, and inhibited growth of spurious bacteria. The focus of low-temperature fermentation in the long run lies in strain optimization, which is to protect and optimize the strains through a variety of methods. Low-temperature fermentation can greatly improve product quality. At present, the most effective methods to promote low-temperature fermentation are gene knockout and probiotic microencapsulation.
Brewery Production Process with Beer Tank and Bottle Full of
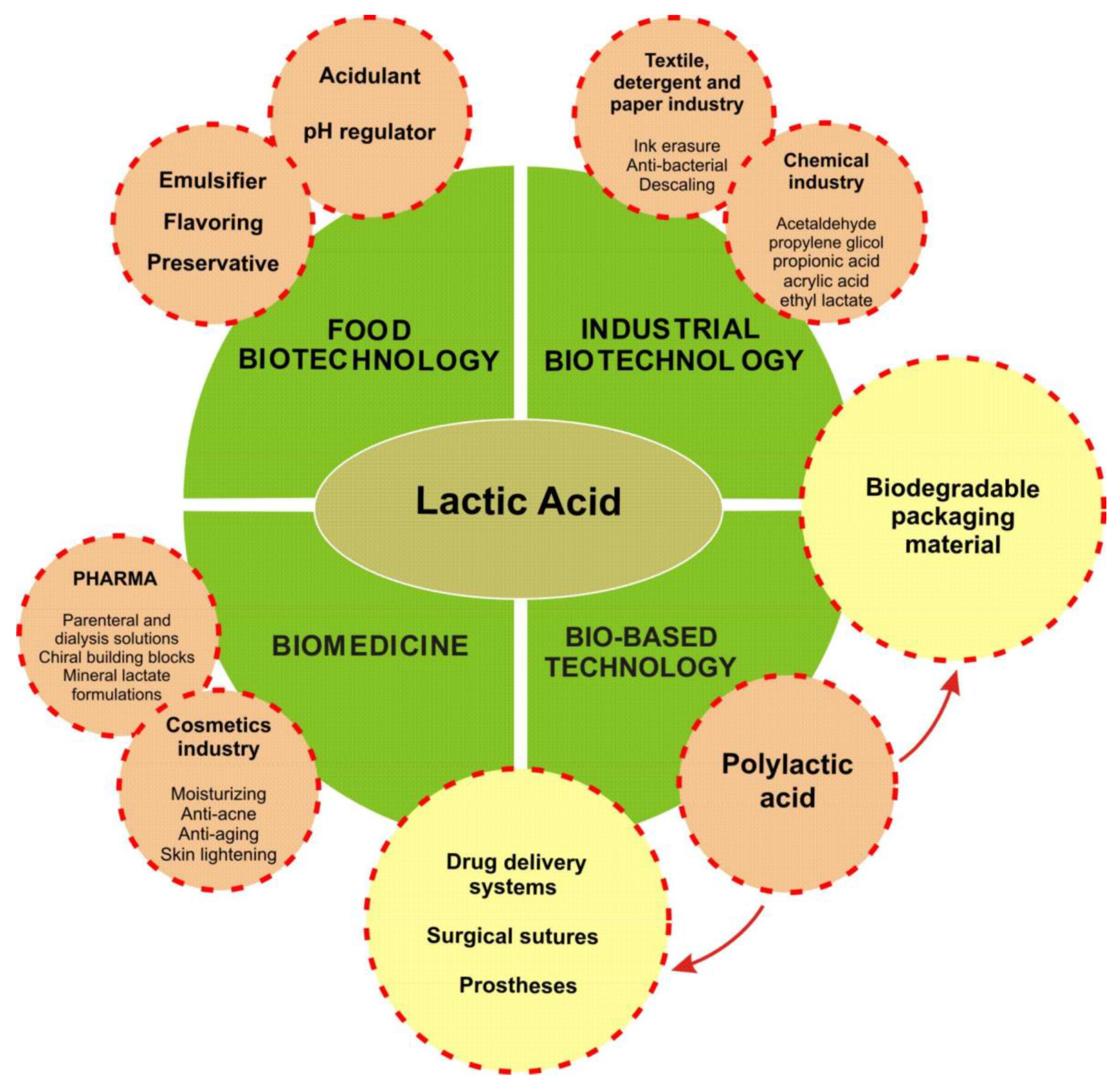
Processes, Free Full-Text
Fermenting Trackers Ferment Log Recipe Tracker Recipe Cards
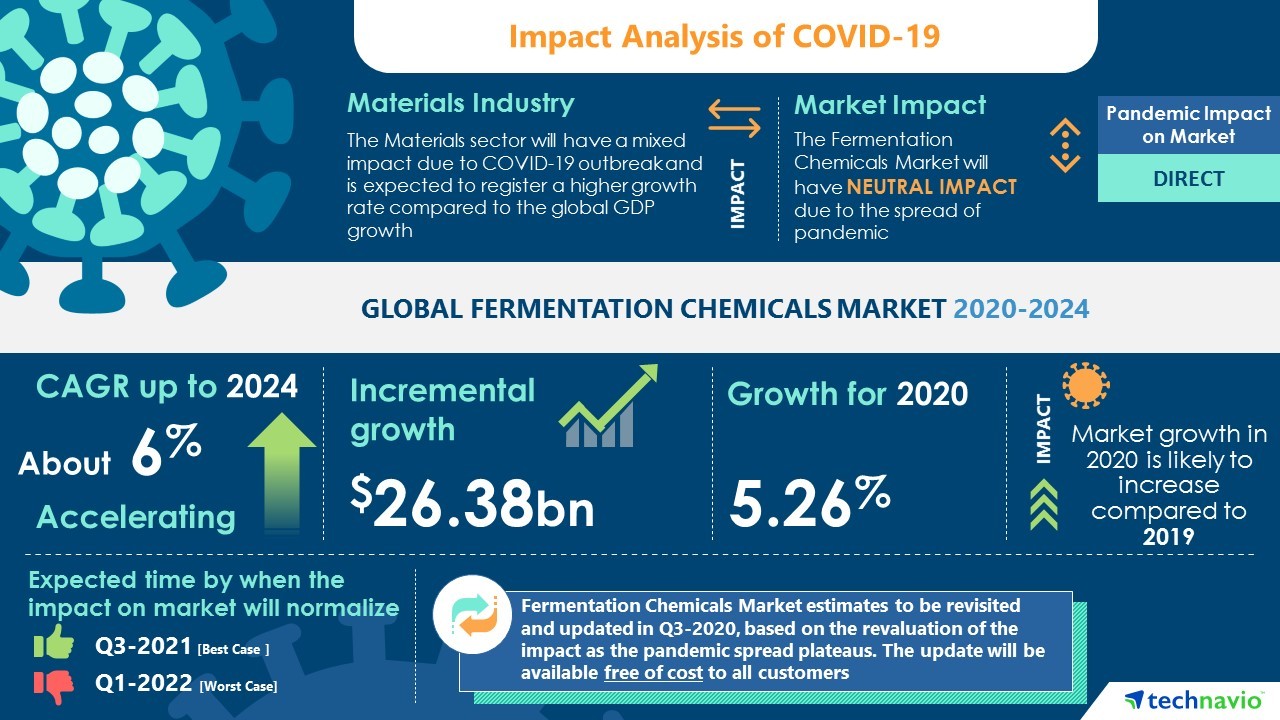
Analysis on Covid-19 Pandemic – Global Fermentation Chemicals
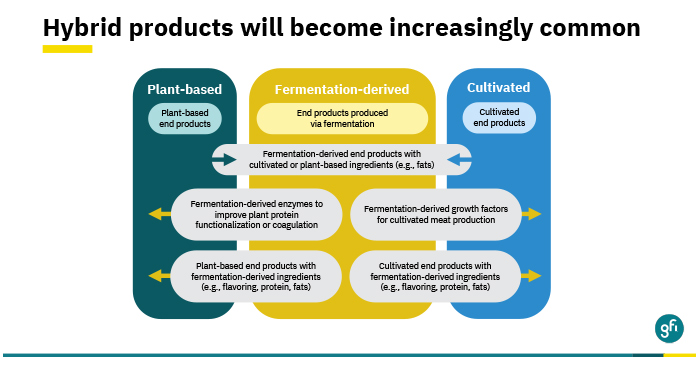
GFI: Alt-Protein Fermentation Tech Ramps Up With Sights Set On
The Art Of Fermentation : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming

Fermentation Fest ATL

Supercharge your health with fermented foods
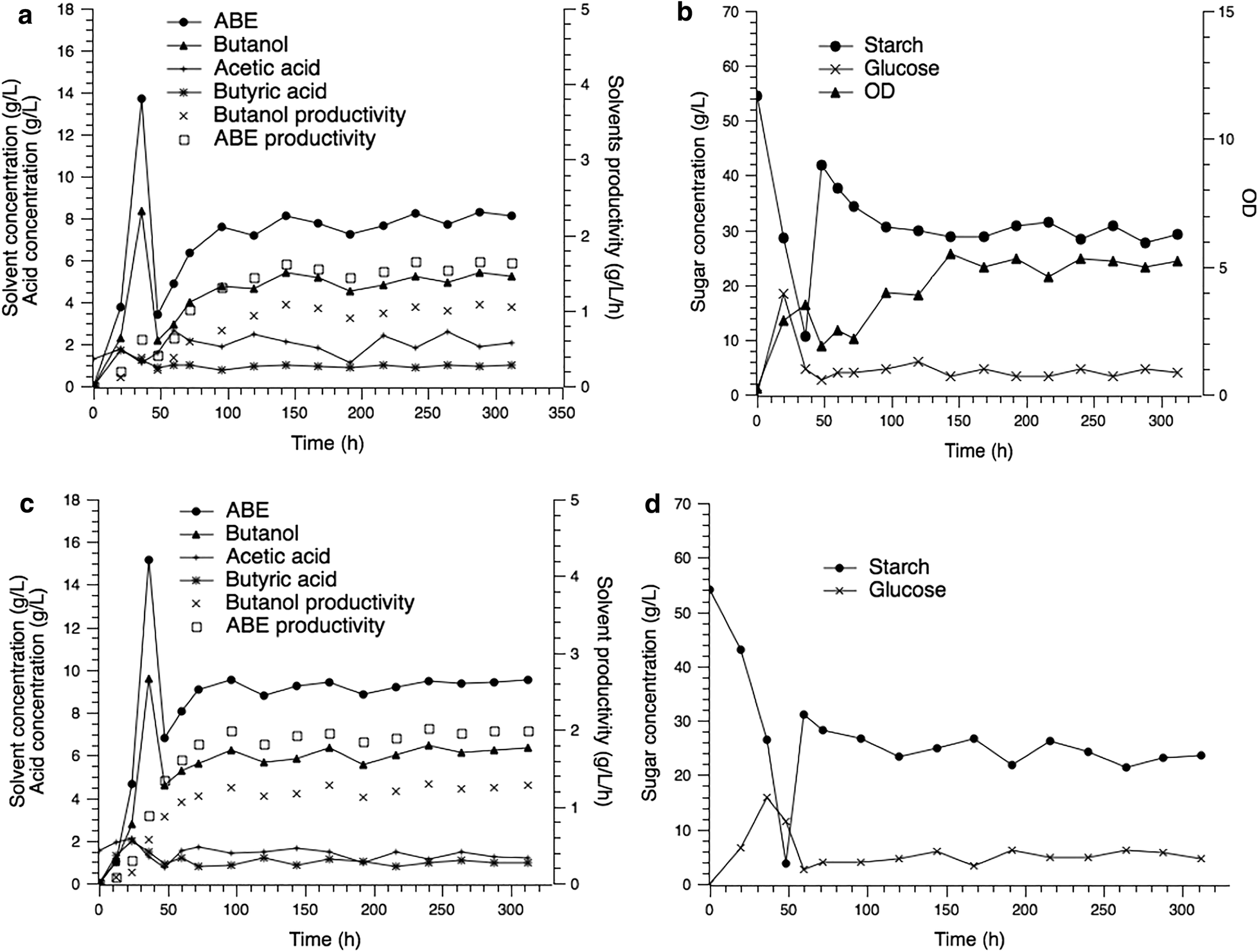
Effective continuous acetone–butanol–ethanol production with full
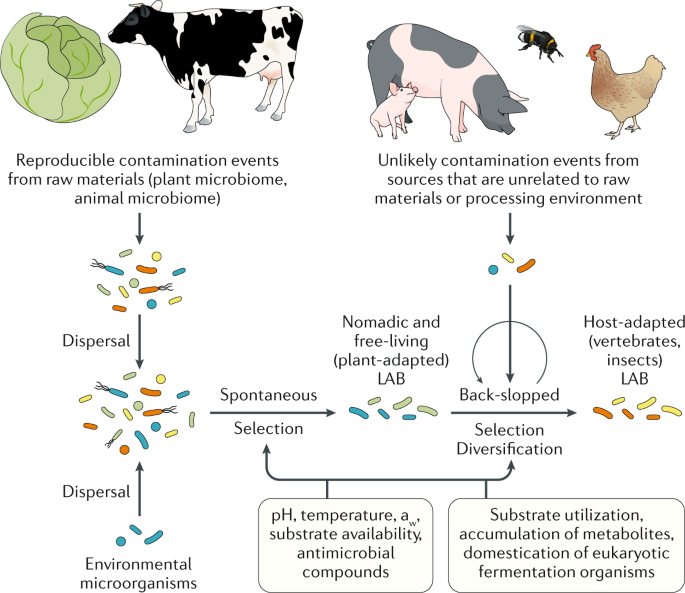
The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and

Brewery Production Process with Beer Tank and Bottle Full of

Fermentation and germination improve nutritional value of cereals

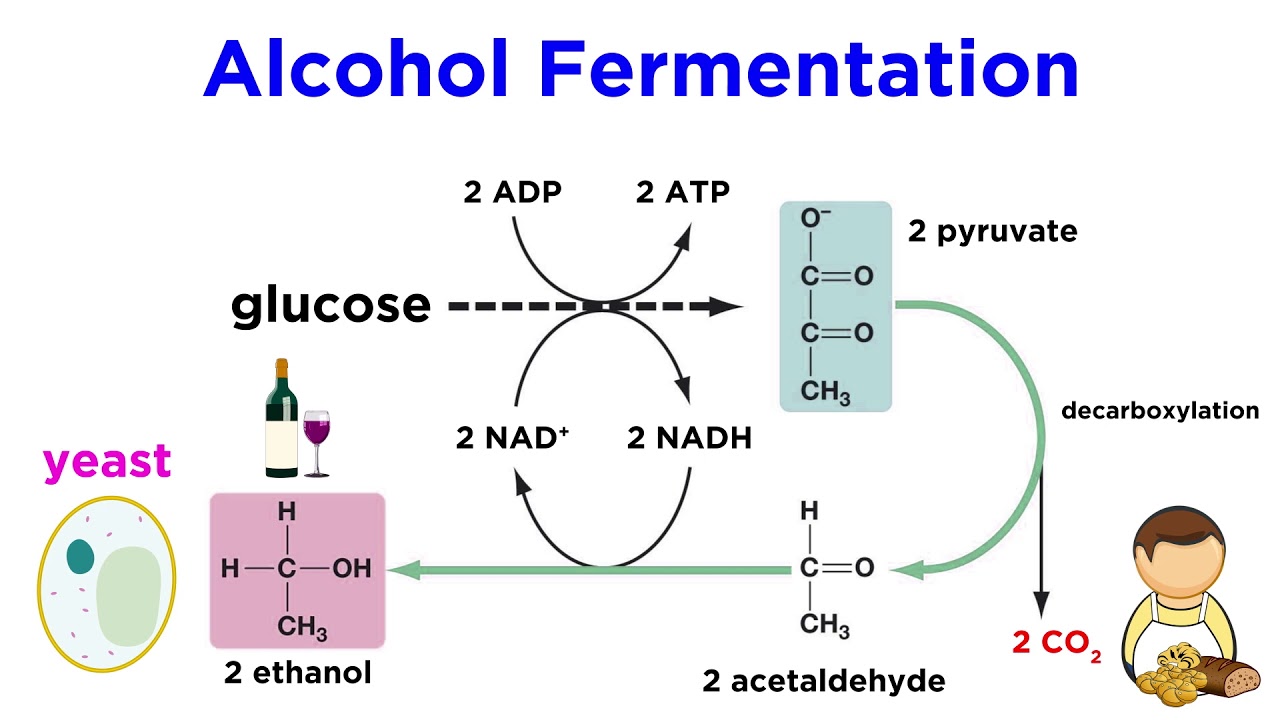
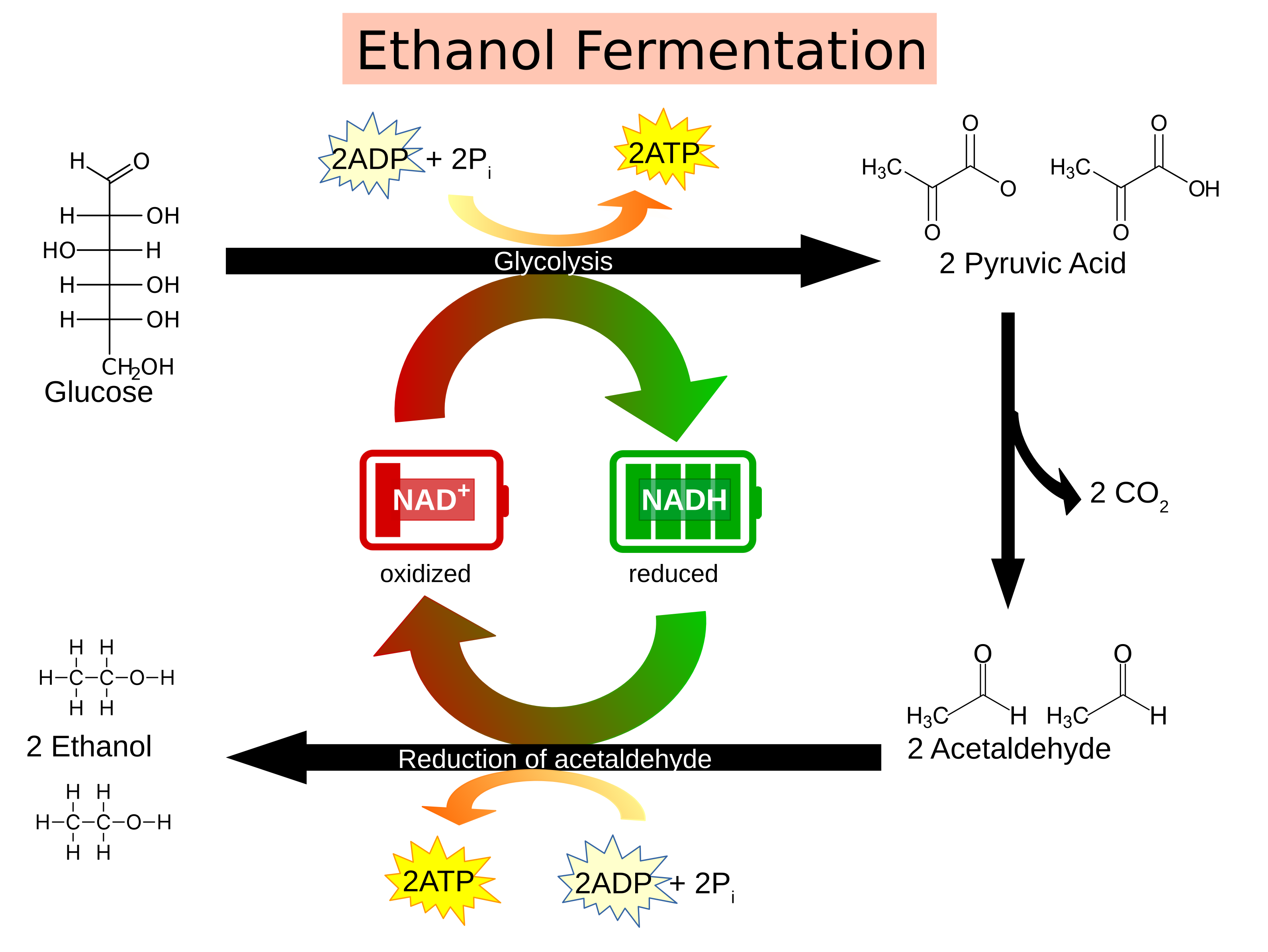
Alcoholic Fermentation by Arthur Harden
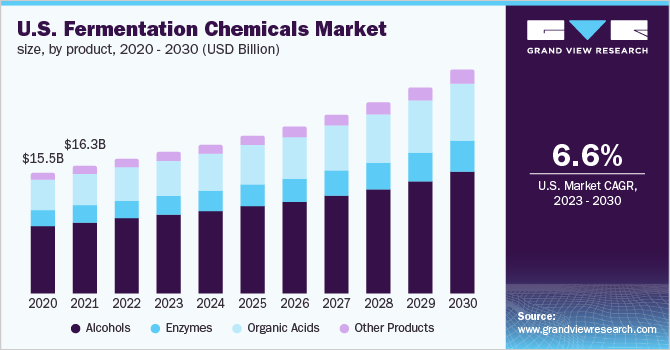
Global Fermentation Chemicals Market Size Report, 2030
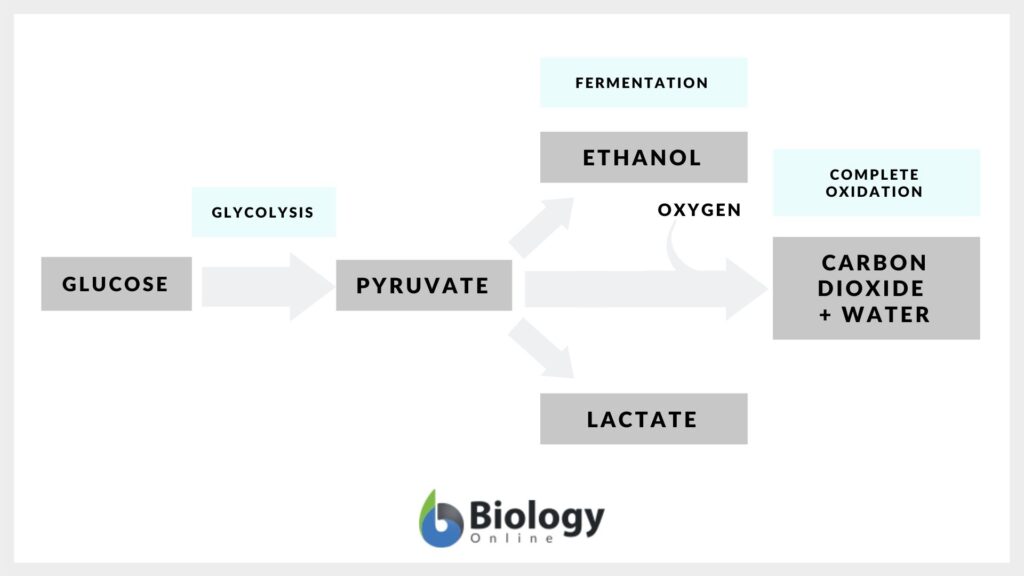
Fermentation - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary