IJMS, Free Full-Text
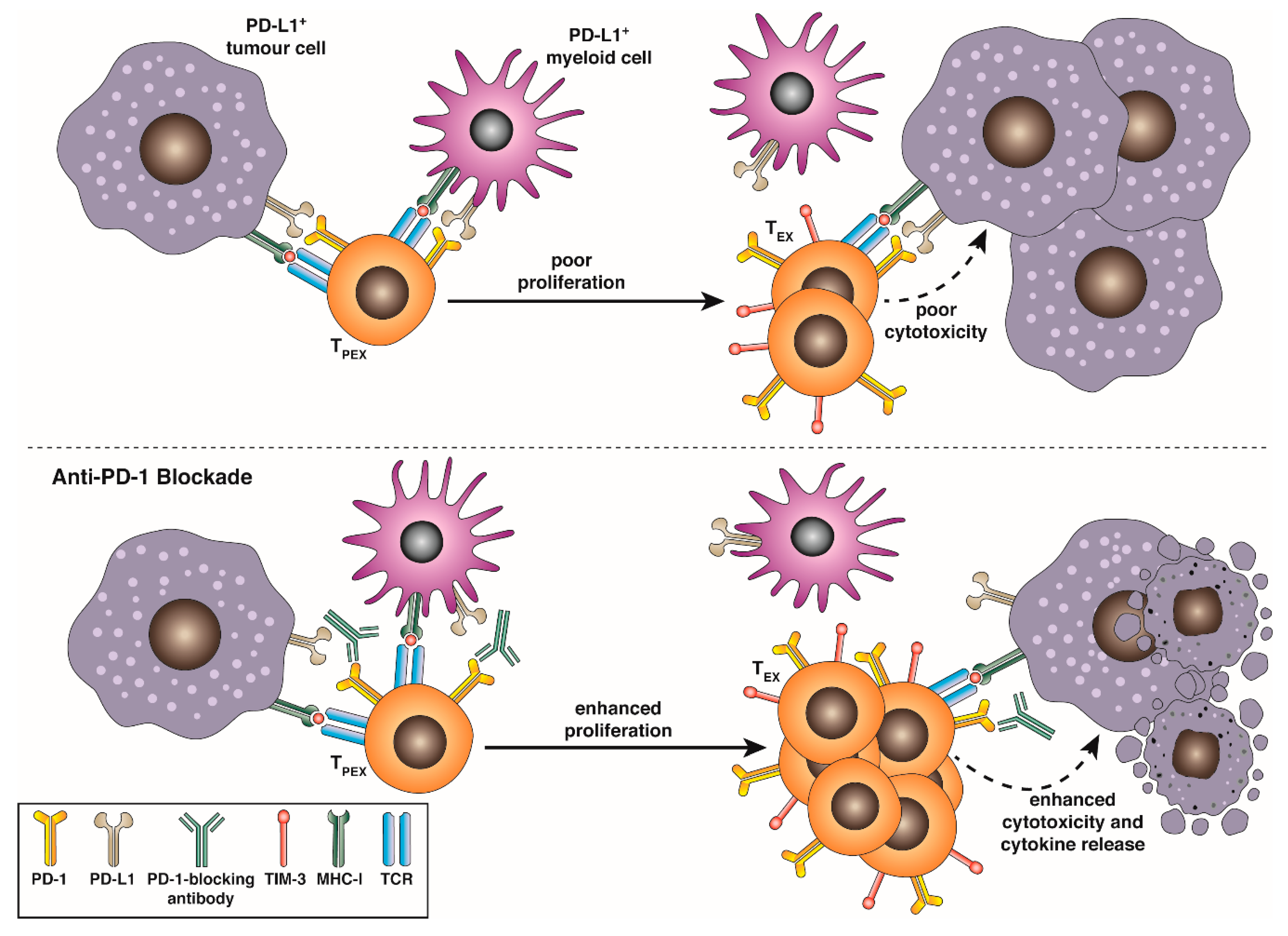
T cells follow a triphasic distinct pathway of activation, proliferation and differentiation before becoming functionally and phenotypically “exhausted” in settings of chronic infection, autoimmunity and in cancer. Exhausted T cells progressively lose canonical effector functions, exhibit altered transcriptional networks and epigenetic signatures and gain constitutive expression of a broad coinhibitory receptor suite. This review outlines recent advances in our understanding of exhausted T cell biology and examines cellular and molecular mechanisms by which a state of dysfunction or exhaustion is established, and mechanisms by which exhausted T cells may still contribute to pathogen or tumour control. Further, this review describes our understanding of exhausted T cell heterogeneity and outlines the mechanisms by which checkpoint blockade differentially engages exhausted T cell subsets to overcome exhaustion and recover T cell function.

International Journal of Molecular Medicine

IJMS, Free Full-Text
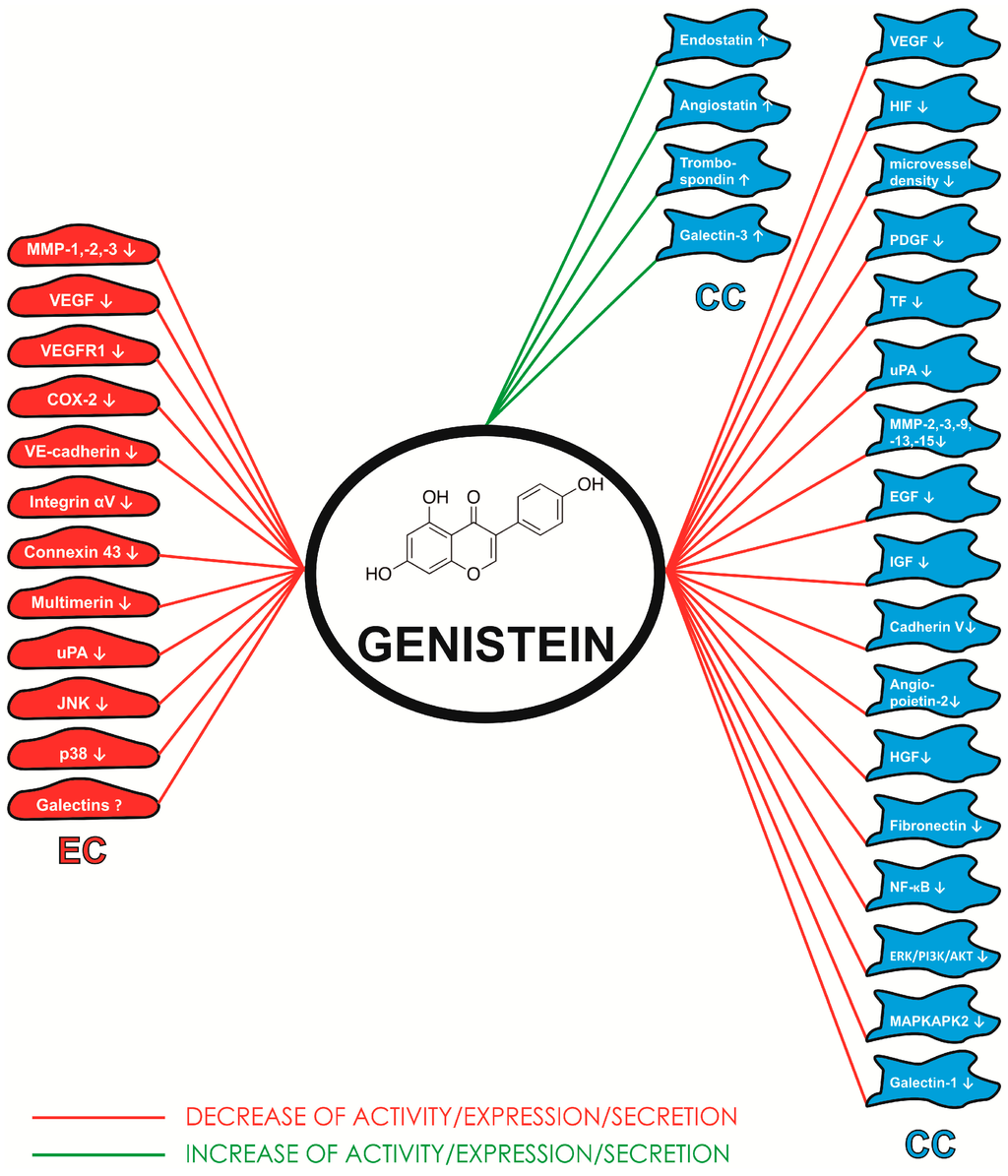
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Ijms Free Full Text Non Invasive Detection Of Extracellular Matrix
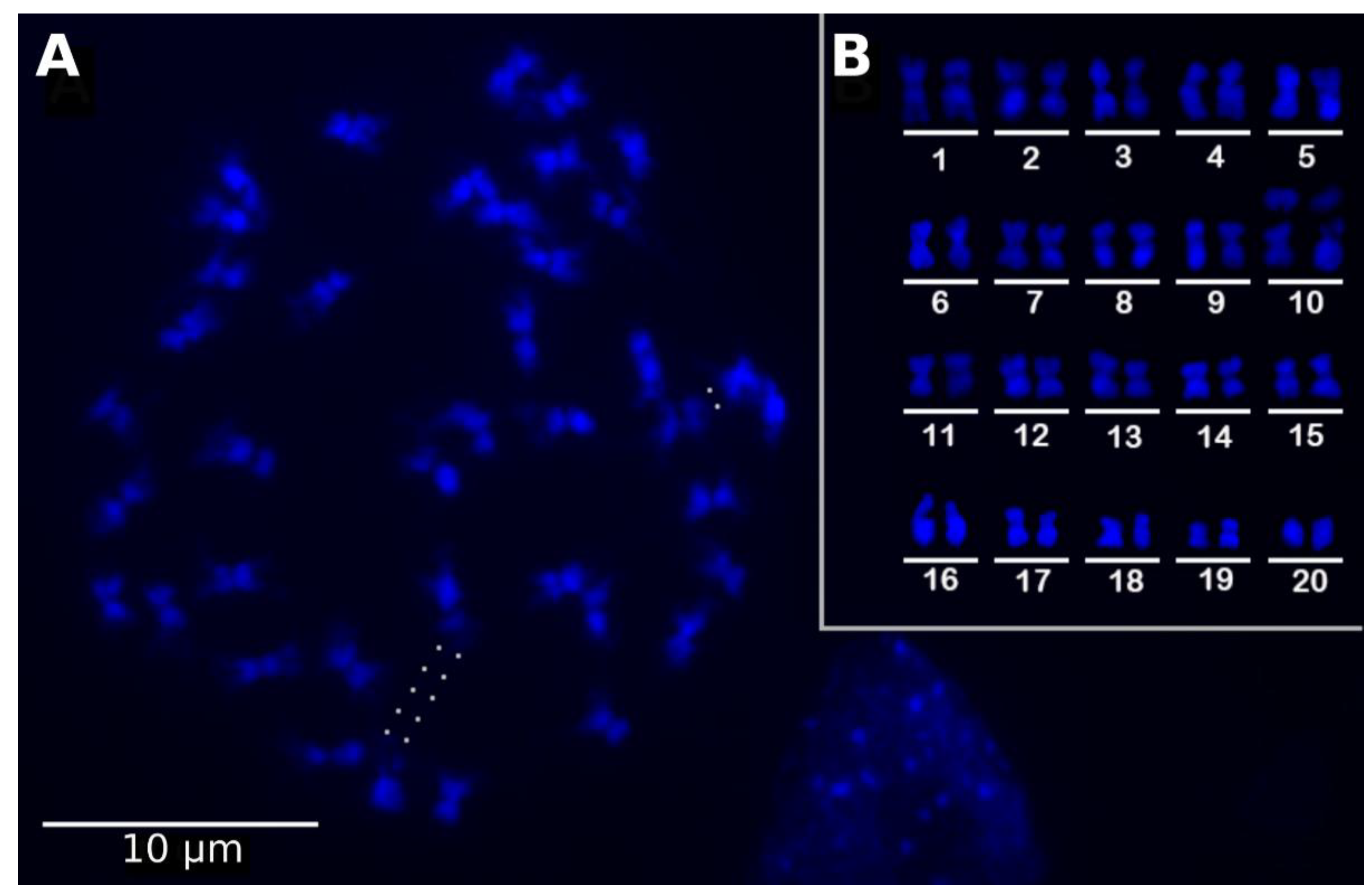
IJMS, Free Full-Text, dmo wiki clon
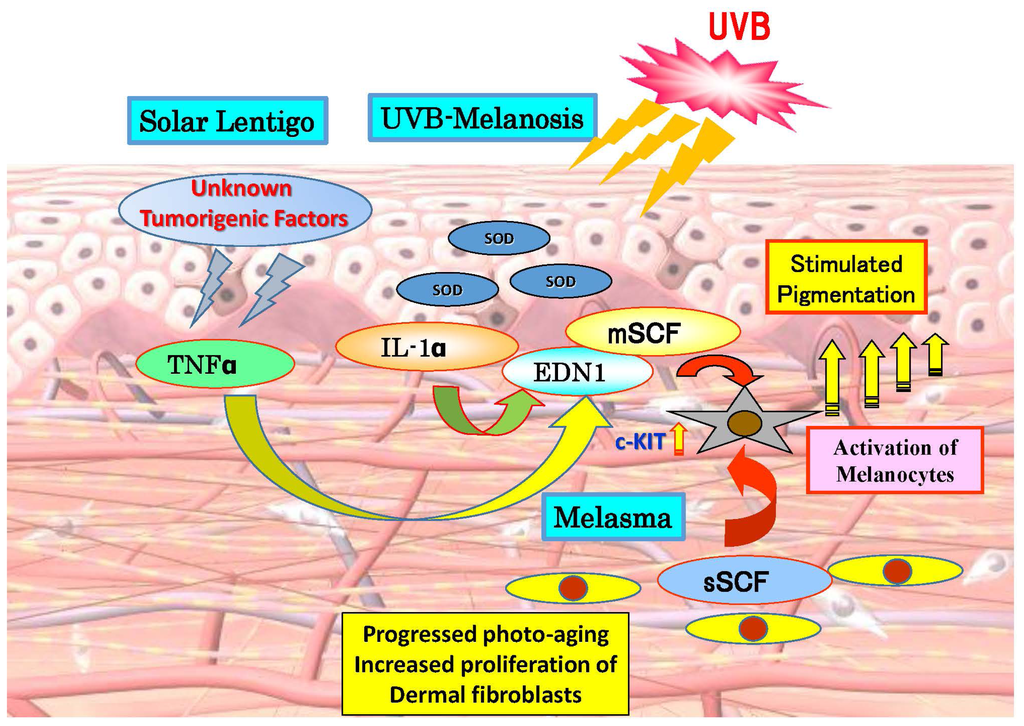
IJMS, Free Full-Text, bronstein meier ii
Submissions International Journal of Medical Students

ISSN 1422-0067 (Online), International journal of molecular sciences

IJMS, Free Full-Text, bronstein meier ii