The Glutamatergic Synapse
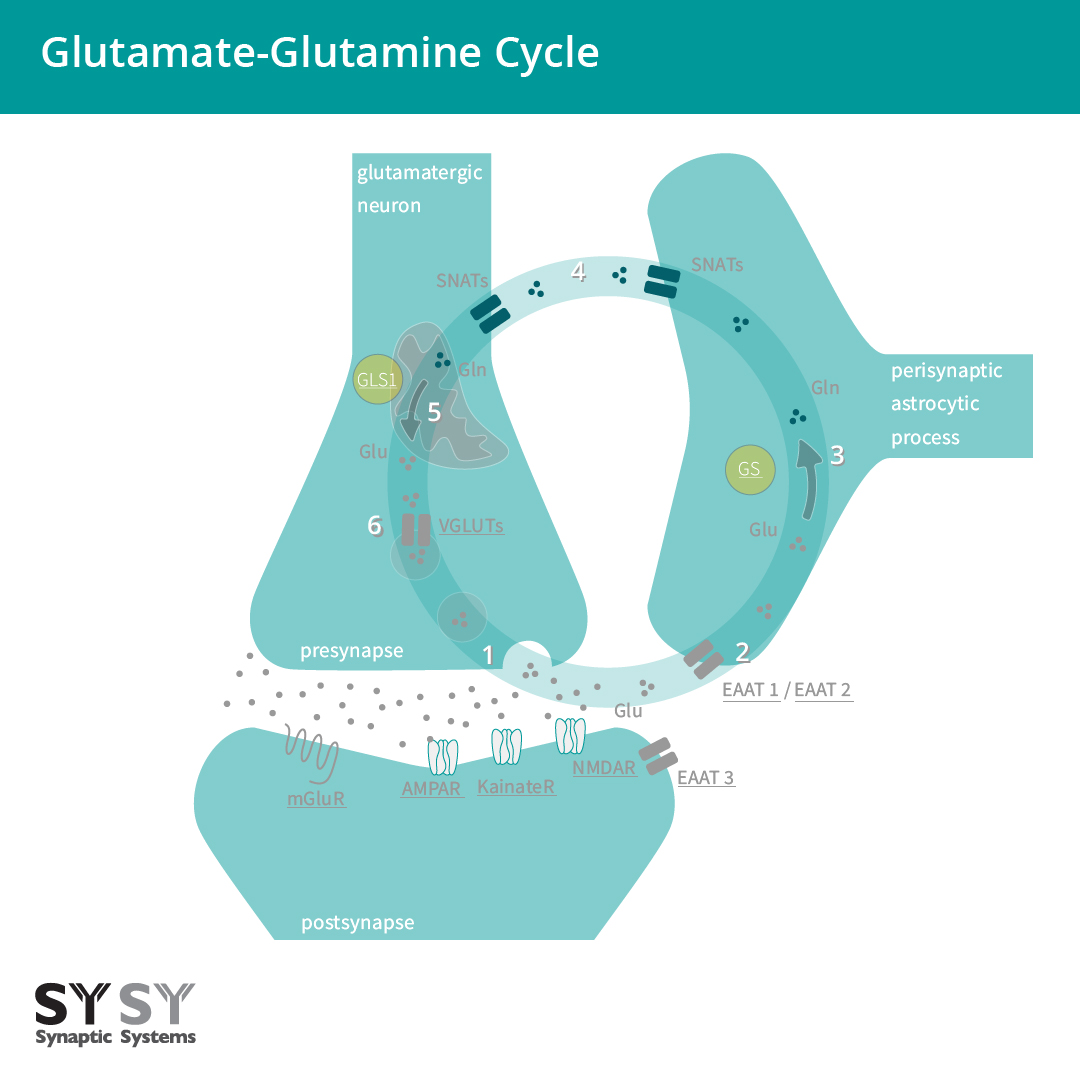
In the mammalian central nervous system (CNS), glutamate is the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter. It is estimated that more than half of all synapses release glutamate and that almost all excitatory neurons in the CNS are glutamatergic.

Presynaptic cGMP sets synaptic strength in the striatum and is important for motor learning

Glutamate Flashcards

Glutamate Transporter Physiology and Function – Dwight Bergles Laboratory

Figure 1, Schematic drawing of a glutamatergic synapse, with postsynaptic AMPA, NMDA, KA and metabotropic receptors - Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies - NCBI Bookshelf

Figure 17, [The ribbon glutamatergic synapse in the retina.]. - Webvision - NCBI Bookshelf

GABA Enhances Transmission at an Excitatory Glutamatergic Synapse
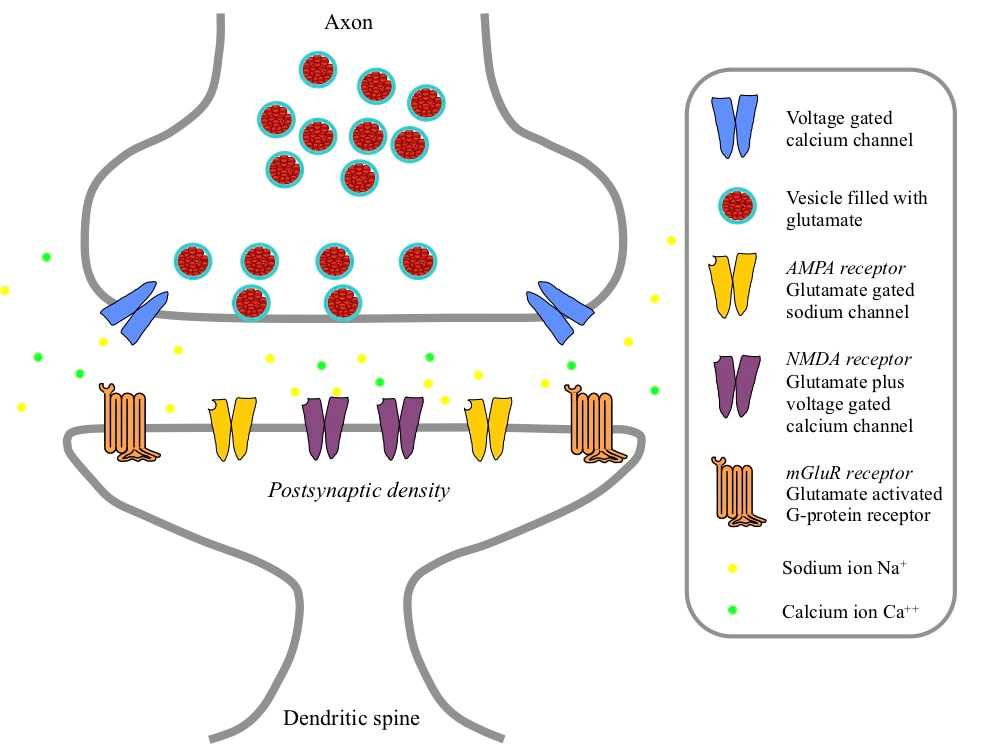
Synaptic chemistry supporting different memory types

Shaping excitation at glutamatergic synapses: Trends in Neurosciences
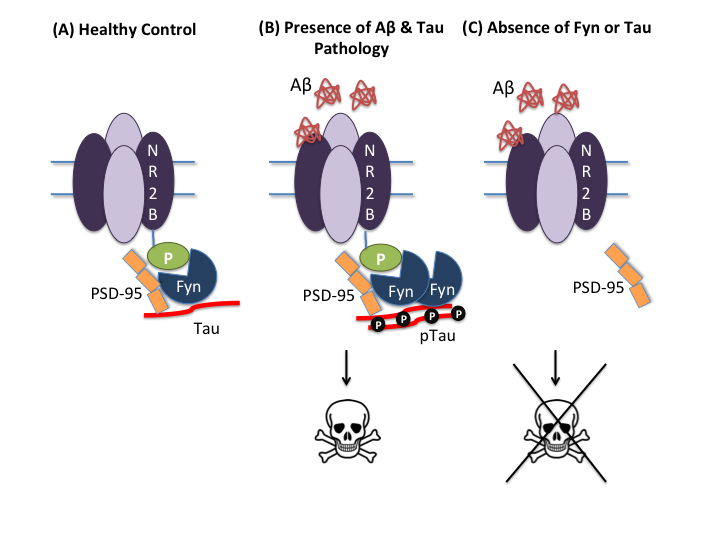
The Role of the Tripartite Glutamatergic Synapse in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease

Input-specific regulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the medial prefrontal cortex by mGlu2/mGlu4 receptor heterodimers

Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Neurological and Psychiatric Diseases: Mechanisms and Prospective - Li-Da Su, Na Wang, Junhai Han, Ying Shen, 2022
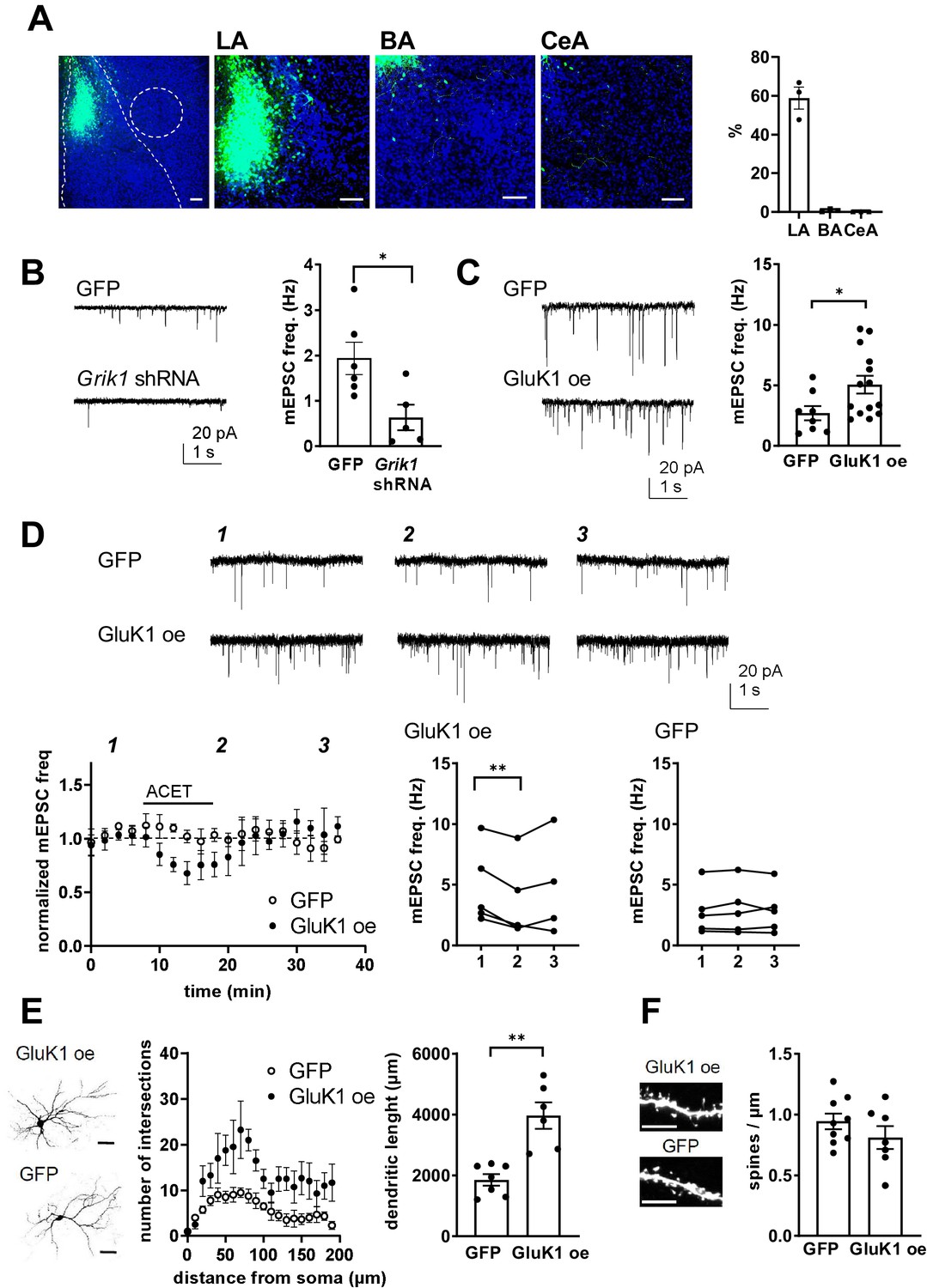
Kainate receptors regulate development of glutamatergic synaptic circuitry in the rodent amygdala

Imaging the glutamate synapse

Glutamatergic and hypothetical aminergic tripartite synapses. The

Cells, Free Full-Text